|
Enriched Uranium, HEU
Enrichment or enriched may refer to: Computing * Data enrichment, appending data with context from other sources; see data management * Enriched text, a text format for email Life sciences * Behavioral enrichment, in animal care * Environmental enrichment, in neuroscience * Paradox of enrichment, in ecology * Use of an enrichment culture to drive growth of a particular microorganism Other uses * Enrichment factor, used to describe bodies of mineral ore * Job enrichment, improving work processes and employee environments * Nuclear enrichment, the process of increasing the concentration of nuclear fuel * Unjust enrichment, in civil law * Enriched category, in mathematics * Chaptalization, a process in winemaking * Food fortification, the process of adding nutrients to cereals or grain * Enrichment in education, activities outside the formal curriculum * Enrichment of breathing gas for scuba diving (e.g. in Nitrox, Enriched Air Nitrox) See also * Cultural enrichment (disambigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
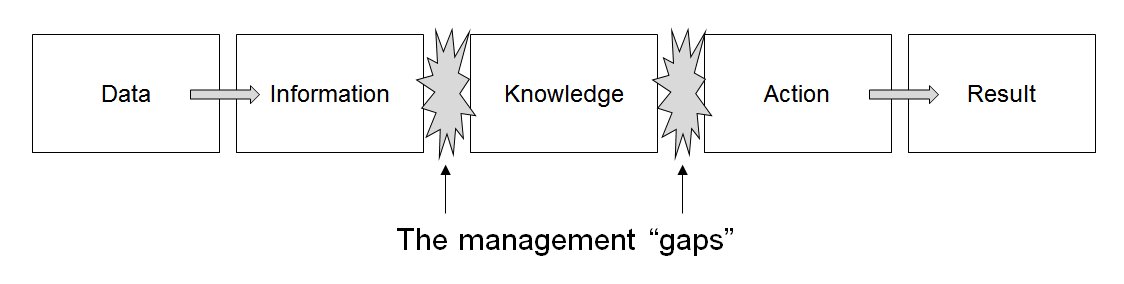
Data Management
Data management comprises all disciplines related to handling data as a valuable resource, it is the practice of managing an organization's data so it can be analyzed for decision making. Concept The concept of data management emerged alongside the evolution of computing technology. In the 1950s, as computers became more prevalent, organizations began to grapple with the challenge of organizing and storing data efficiently. Early methods relied on punch cards and manual sorting, which were labor-intensive and prone to errors. The introduction of database management systems in the 1970s marked a significant milestone, enabling structured storage and retrieval of data. By the 1980s, relational database models revolutionized data management, emphasizing the importance of data as an asset and fostering a data-centric mindset in business. This era also saw the rise of data governance practices, which prioritized the organization and regulation of data to ensure quality and complian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unjust Enrichment
Restitution and unjust enrichment is the field of law relating to gains-based recovery. In contrast with damages (the law of compensation), restitution is a claim or remedy requiring a defendant to give up benefits wrongfully obtained. Liability for restitution is primarily governed by the "principle of unjust enrichment": A person who has been unjustly enriched at the expense of another is required to make restitution. This principle derives from late Roman law, as stated in the Latin maxim attributed to Sextus Pomponius, ''Jure naturae aequum est neminem cum alterius detrimentum et injuria fieri locupletiorem'' ("By natural law it is just that no one should be enriched by another's loss or injury"). In civil law systems, it is also referred to as enrichment without cause or unjustified enrichment. In pre-modern English common law, restitutionary claims were often brought in an action for '' assumpsit'' and later in a claim for money had and received. The seminal case giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Enrichment (other)
Cultural enrichment can refer to: * The generally understood objective within Arts in education to expose children to the arts * Culture change, a term used in public policy making that regards the role of culture on individual and community behavior * Cultural pluralism, when a society has subset groups that maintain a unique cultural identity and values ** Acculturation, a process of culture change that describes how members of a minority culture adapt to the prevailing societal culture ** Multiculturalism, a term in sociology which is synonymous with ethnic pluralism * Cultural diffusion, a concept by Leo Frobenius where culture is shared between individuals * Cultural diplomacy, a type of diplomacy which is a cultural exchange among different nations * Cultural appropriation Cultural appropriation is the adoption of an element or elements of one culture or cultural identity, identity by members of another culture or identity in a manner perceived as inappropriate or u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrox
Nitrox refers to any gas mixture composed (excepting trace gases) of nitrogen and oxygen. It is usually used for mixtures that contain less than 78% nitrogen by volume. In the usual application, underwater diving, nitrox is normally distinguished from air and handled differently. The most common use of nitrox mixtures containing oxygen in higher proportions than atmospheric air is in scuba diving, where the reduced partial pressure of nitrogen is advantageous in reducing nitrogen uptake in the body's tissues, thereby extending the practicable underwater dive time by reducing the decompression requirement, or reducing the risk of decompression sickness (also known as ''the bends''). The two most common recreational diving nitrox mixes are 32% and 36% oxygen, which have maximum operating depths of about 110 feet (34 meters) and 95 feet (29 meters) respectively. Nitrox is used to a lesser extent in surface-supplied diving, as these advantages are reduced by the more complex logi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education
Education is the transmission of knowledge and skills and the development of character traits. Formal education occurs within a structured institutional framework, such as public schools, following a curriculum. Non-formal education also follows a structured approach but occurs outside the formal schooling system, while informal education involves unstructured learning through daily experiences. Formal and non-formal education are categorized into levels, including early childhood education, primary education, secondary education, and tertiary education. Other classifications focus on teaching methods, such as teacher-centered and student-centered education, and on subjects, such as science education, language education, and physical education. Additionally, the term "education" can denote the mental states and qualities of educated individuals and the academic field studying educational phenomena. The precise definition of education is disputed, and there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Fortification
Food fortification is the addition of micronutrients (essential trace elements and vitamins) to food products. Food enrichment specifically means adding back nutrients lost during food processing, while fortification includes adding nutrients not naturally present.World Health Organization and Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Guidelines on food fortification with micronutrients. 2006 ited on 2011 Oct 30 Food manufacturers and governments have used these practices since the 1920s to help prevent nutrient deficiencies in populations. Comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaptalization
Chaptalization is the process of adding sugar to unfermented grape must in order to increase the alcohol content after fermentation. The technique is named after its developer, the French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal. This process is not intended to make the wine sweeter, but rather to provide more sugar for the yeast to ferment into alcohol. Chaptalization has generated controversy and discontent in the French wine industry due to advantages that the process is perceived to give producers in poor-climate areas. In response to violent demonstrations by protesters in 1907, the French government began regulating the amount of sugar that can be added to wine. Chaptalization is sometimes referred to as enrichment, for example in the European Union wine regulations specifying the legality of the practice within EU. The legality of chaptalization varies by country, region, and even wine type. In general, it is legal in regions that produce grapes with low sugar content, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enriched Category
In category theory, a branch of mathematics, an enriched category generalizes the idea of a category (mathematics), category by replacing hom-sets with objects from a general monoidal category. It is motivated by the observation that, in many practical applications, the hom-set often has additional structure that should be respected, e.g., that of being a vector space of morphisms, or a topological space of morphisms. In an enriched category, the set of morphisms (the hom-set) associated with every pair of objects is replaced by an object (category theory), object in some fixed monoidal category of "hom-objects". In order to emulate the (associative) composition of morphisms in an ordinary category, the hom-category must have a means of composing hom-objects in an associative manner: that is, there must be a binary operation on objects giving us at least the structure of a monoidal category, though in some contexts the operation may also need to be commutative and perhaps also to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Enrichment
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (238U with 99.2732–99.2752% natural abundance), uranium-235 (235U, 0.7198–0.7210%), and uranium-234 (234U, 0.0049–0.0059%). 235U is the only nuclide existing in nature (in any appreciable amount) that is fissile with thermal neutrons. Enriched uranium is a critical component for both civil nuclear power generation and military nuclear weapons. Low-enriched uranium (20% 235U, typically >85%) is used for the cores of many nuclear weapons, as well as compact reactors for naval propulsion and research, as well as breeder reactors. There are about 2,000 tonnes of highly enriched uranium in the world. Enrichment methods were first developed on a large scale by the Manhattan Project. Its gaseous diffusion method was used in the 1940s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enriched Text
Enriched text is a formatted text format for email, defined by the IETF in RFC 1896 and associated with the text/enriched MIME type which is defined in RFC 1563. Format It is "intended to facilitate the wider interoperation of simple enriched text across a wide variety of hardware and software platforms". As of 2012, enriched text remained almost unknown in email traffic, while HTML email is widely used. Enriched text, or at least the subset of HTML that can be transformed into enriched text, is seen as preferable to full HTML for use with email (mainly because of security considerations). A predecessor of this MIME type was called text/richtext in RFC 1341 and RFC 1521. Neither should be confused with Rich Text Format (RTF, MIME type text/rtf or application/rtf) which are unrelated specifications, devised by Microsoft. A single newline in enriched text is treated as a space. Formatting commands are in the same style as SGML and HTML Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Job Enrichment
Job enrichment is a method of motivating employees where a job is designed to have interesting and challenging tasks which can require more skill and can increase pay. Origin Frederick Herzberg, an American psychologist, originally developed the concept of 'job enrichment' in 1968, in an article that he published on pioneering studies at AT&T.Frederick Herzberg, HBR Jan 2003, One More Time: How Do You Motivate Employees? Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2003/01/one-more-time-how-do-you-motivate-employees/ar/1 The concept stemmed from Herzberg's motivator-hygiene theory, which is based on the premise that job attitude is a construct of two independent factors, namely job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction. Job satisfaction encompasses intrinsic factors which arise from the work itself, including achievement and advancement, whilst job dissatisfaction stems from factors external to the actual work, including company policy and the quality of supervision. He came up with this term w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enrichment Factor
Enrichment factor is used to describe bodies of mineral ore. It is defined as the minimum factor by which the weight percent of mineral in an orebody is greater than the average occurrence of that mineral in the Earth's crust. It can be used to compare the necessary enrichment of different types of minerals for their recovery to be economically viable. Determining enrichment factors Enrichment Factors that relate to the economic viability of an orebody are largely determined by the following: *The value of the mineral (the higher the value of the recovered mineral the more expensive the recovery process can be in order to obtain it - this could include processing larger amounts of ore) *The level of the technology available to recover the mineral (any advances in technology may allow ores with lower wt% mineral to be exploited for the same cost) *The cost of refining the mineral once recovered (this may require the bulk of the price demanded by the final product, so leaving little m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |